强化学习——Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG)¶
作者::EastSmith
日期: 2021.10
AI Studio项目:点击体验
一、介绍¶
深度确定策略梯度(Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient,DDPG)¶
它是一种学习连续动作的无模型策略算法。
它结合了DPG(确定性策略梯度)和DQN(深度Q网络)的思想。它利用DQN中的经验重放和延迟更新的目标网络,并基于DPG,可以在连续的动作空间上运行。
要解决的问题¶
你正试图解决经典的倒立摆控制问题。在此设置中,你只能执行两个操作:向左摆动或向右摆动。
对于Q-学习算法来说,这个问题的挑战在于动作是连续的而不是离散的。也就是说,你必须从-2到+2的无限操作中进行选择,而不是使用像-1或+1这样的两个离散操作。
快速理论¶
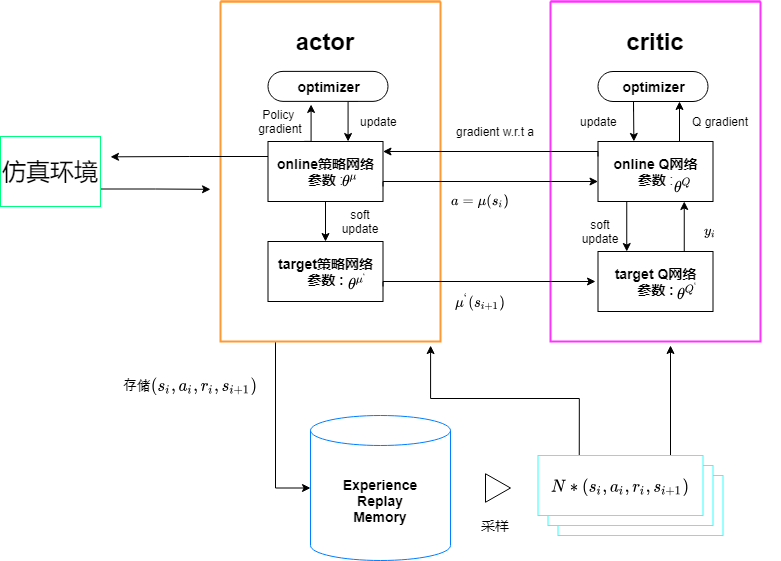
就像演员-评论家的方法一样,它有两个网络:
演员-它提出一个给定状态的动作。
评论家-它预测给定的状态和动作是好(正值)还是坏(负值)。
DDPG使用的另外2种技术: 首先,它使用两个目标网络。
为什么?因为它增加了训练的稳定性。简言之,它是从估计的目标和目标网络学习更新,从而保持它估计的目标稳定。
从概念上讲,这就像是说,“我有一个如何玩这个好主意,我要尝试一下,直到我找到更好的东西”,而不是说“我要在每一个动作之后重新学习如何玩好整个游戏”。
第二,使用经验回放。
它存储元组列表(状态、动作、奖励、下一个状态),而不是仅仅从最近的经验中学习,而是从取样中学习到迄今为止积累的所有经验。
现在,看看它是如何实现的。¶
二、环境配置¶
本教程基于Paddle 2.2.0-rc0 编写,如果您的环境不是本版本,请先参考官网安装 Paddle 2.2.0-rc0。
import gym
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
from itertools import count
from paddle.distribution import Normal
import numpy as np
from collections import deque
import random
import paddle.nn.functional as F
from visualdl import LogWriter
三、实施深度确定策略梯度网络(Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient,DDPG)¶
这里定义了演员和评论家网络。这些都是具有ReLU激活的基本全连接模型。
注意:你需要为Actor的最后一层使用tanh激活,将值映射到-1到1之间。Memory类定义了经验回放池。
# 定义评论家网络结构
# DDPG这种方法与Q学习紧密相关,可以看作是连续动作空间的深度Q学习。
class Critic(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(Critic, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(3, 256)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256 + 1, 128)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(128, 1)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x, a):
x = self.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = paddle.concat((x, a), axis=1)
x = self.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
# 定义演员网络结构
# 为了使DDPG策略更好地进行探索,在训练时对其行为增加了干扰。 原始DDPG论文的作者建议使用时间相关的 OU噪声 ,
# 但最近的结果表明,不相关的均值零高斯噪声效果很好。 由于后者更简单,因此是首选。
class Actor(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, is_train=True):
super(Actor, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(3, 256)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(128, 1)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.tanh = nn.Tanh()
self.noisy = Normal(0, 0.2)
self.is_train = is_train
def forward(self, x):
x = self.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.tanh(self.fc3(x))
return x
def select_action(self, epsilon, state):
state = paddle.to_tensor(state,dtype="float32").unsqueeze(0)
with paddle.no_grad():
action = self.forward(state).squeeze() + self.is_train * epsilon * self.noisy.sample([1]).squeeze(0)
return 2 * paddle.clip(action, -1, 1).numpy()
# 重播缓冲区:这是智能体以前的经验, 为了使算法具有稳定的行为,重播缓冲区应该足够大以包含广泛的体验。
# 如果仅使用最新数据,则可能会过分拟合,如果使用过多的经验,则可能会减慢模型的学习速度。 这可能需要一些调整才能正确。
class Memory(object):
def __init__(self, memory_size: int) -> None:
self.memory_size = memory_size
self.buffer = deque(maxlen=self.memory_size)
def add(self, experience) -> None:
self.buffer.append(experience)
def size(self):
return len(self.buffer)
def sample(self, batch_size: int, continuous: bool = True):
if batch_size > len(self.buffer):
batch_size = len(self.buffer)
if continuous:
rand = random.randint(0, len(self.buffer) - batch_size)
return [self.buffer[i] for i in range(rand, rand + batch_size)]
else:
indexes = np.random.choice(np.arange(len(self.buffer)), size=batch_size, replace=False)
return [self.buffer[i] for i in indexes]
def clear(self):
self.buffer.clear()
四、训练模型¶
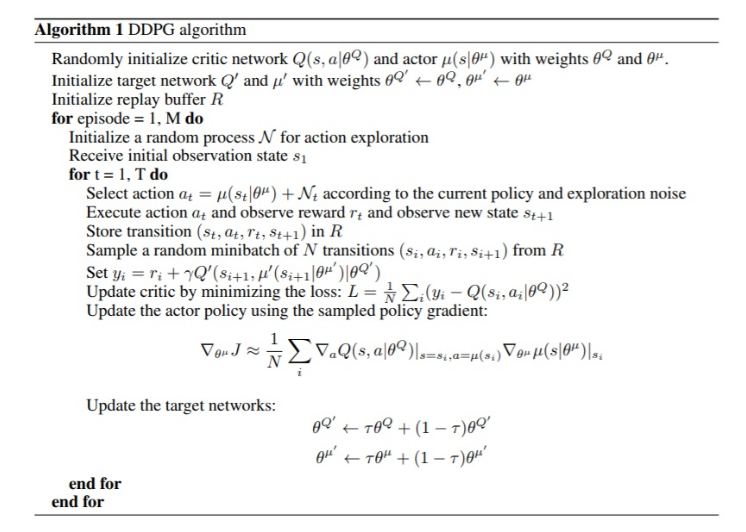
算法伪代码¶
# 定义软更新的函数
def soft_update(target, source, tau):
for target_param, param in zip(target.parameters(), source.parameters()):
target_param.set_value( target_param * (1.0 - tau) + param * tau)
# 定义环境、实例化模型
env = gym.make('Pendulum-v1')
actor = Actor()
critic = Critic()
actor_target = Actor()
critic_target = Critic()
# 定义优化器
critic_optim = paddle.optimizer.Adam(parameters=critic.parameters(), learning_rate=3e-5)
actor_optim = paddle.optimizer.Adam(parameters=actor.parameters(), learning_rate=1e-5)
# 定义超参数
explore = 50000
epsilon = 1
gamma = 0.99
tau = 0.001
memory_replay = Memory(50000)
begin_train = False
batch_size = 32
learn_steps = 0
epochs = 250
writer = LogWriter('logs')
# 训练循环
for epoch in range(0, epochs):
state = env.reset()
episode_reward = 0
for time_step in range(200):
action = actor.select_action(epsilon, state)
next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step([action])
episode_reward += reward
reward = (reward + 8.1) / 8.1
memory_replay.add((state, next_state, action, reward))
if memory_replay.size() > 1280:
learn_steps += 1
if not begin_train:
print('train begin!')
begin_train = True
experiences = memory_replay.sample(batch_size, False)
batch_state, batch_next_state, batch_action, batch_reward = zip(*experiences)
batch_state = paddle.to_tensor(batch_state,dtype="float32")
batch_next_state = paddle.to_tensor(batch_next_state,dtype="float32")
batch_action = paddle.to_tensor(batch_action,dtype="float32").unsqueeze(1)
batch_reward = paddle.to_tensor(batch_reward,dtype="float32").unsqueeze(1)
# 均方误差 y - Q(s, a) , y是目标网络所看到的预期收益, 而 Q(s, a)是Critic网络预测的操作值。
# y是一个移动的目标,评论者模型试图实现的目标;这个目标通过缓慢的更新目标模型来保持稳定。
with paddle.no_grad():
Q_next = critic_target(batch_next_state, actor_target(batch_next_state))
Q_target = batch_reward + gamma * Q_next
critic_loss = F.mse_loss(critic(batch_state, batch_action), Q_target)
critic_optim.clear_grad()
critic_loss.backward()
critic_optim.step()
writer.add_scalar('critic loss', critic_loss.numpy(), learn_steps)
# 使用Critic网络给定值的平均值来评价Actor网络采取的行动。 我们力求使这一数值最大化。
# 因此,我们更新了Actor网络,对于一个给定状态,它产生的动作尽量让Critic网络给出高的评分。
critic.eval()
actor_loss = - critic(batch_state, actor(batch_state))
# print(actor_loss.shape)
actor_loss = actor_loss.mean()
actor_optim.clear_grad()
actor_loss.backward()
actor_optim.step()
critic.train()
writer.add_scalar('actor loss', actor_loss.numpy(), learn_steps)
soft_update(actor_target, actor, tau)
soft_update(critic_target, critic, tau)
if epsilon > 0:
epsilon -= 1 / explore
state = next_state
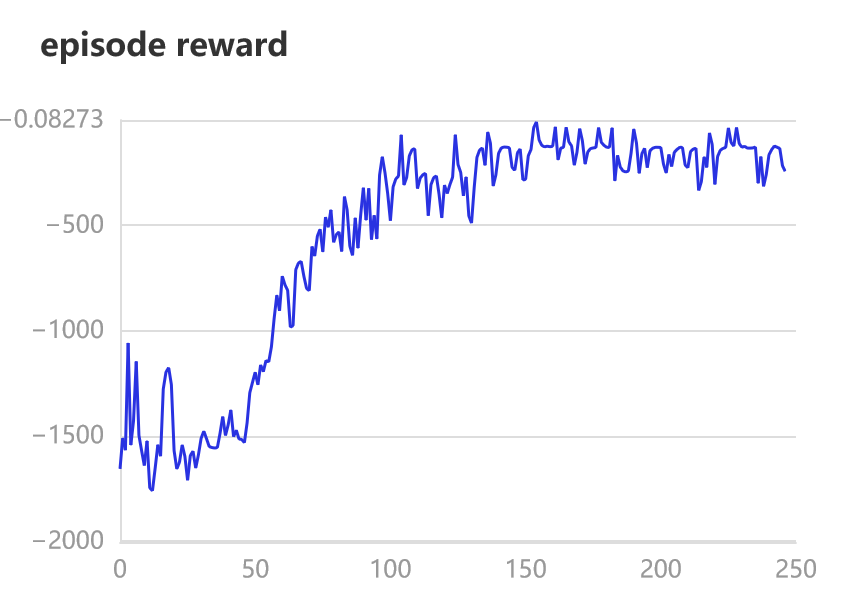
writer.add_scalar('episode reward', episode_reward, epoch)
if epoch % 50 == 0:
print('Epoch:{}, episode reward is {}'.format(epoch, episode_reward))
if epoch % 200 == 0:
paddle.save(actor.state_dict(), 'model/ddpg-actor' + str(epoch) + '.para')
paddle.save(critic.state_dict(), 'model/ddpg-critic' + str(epoch) + '.para')
print('model saved!')
Epoch:0, episode reward is -1233.9451882846902
model saved!
train begin!
六、总结和建议¶
DDPG中同时用到了“基于价值”与“基于策略”这两种思想。
experience replay memory的使用:actor同环境交互时,产生的transition数据序列是在时间上高度关联的,如果这些数据序列直接用于训练,会导致神经网络的过拟合,不易收敛。 DDPG的actor将transition数据先存入经验缓冲池, 然后在训练时,从经验缓冲池中随机采样mini-batch数据,这样采样得到的数据可以认为是无关联的。
target 网络和online 网络的使用, 使得学习过程更加稳定,收敛更有保障。
如果训练进行的正确,平均奖励将随着时间的推移而增加。请随意尝试演员和评论家网络的不同学习率、tau值和架构。
倒立摆问题的复杂度较低,但DDPG在许多其它问题上都有很好的应用。另一个很好的环境是LunarLandingContinuous-v2,但是需要更多的训练才能获得好的效果。